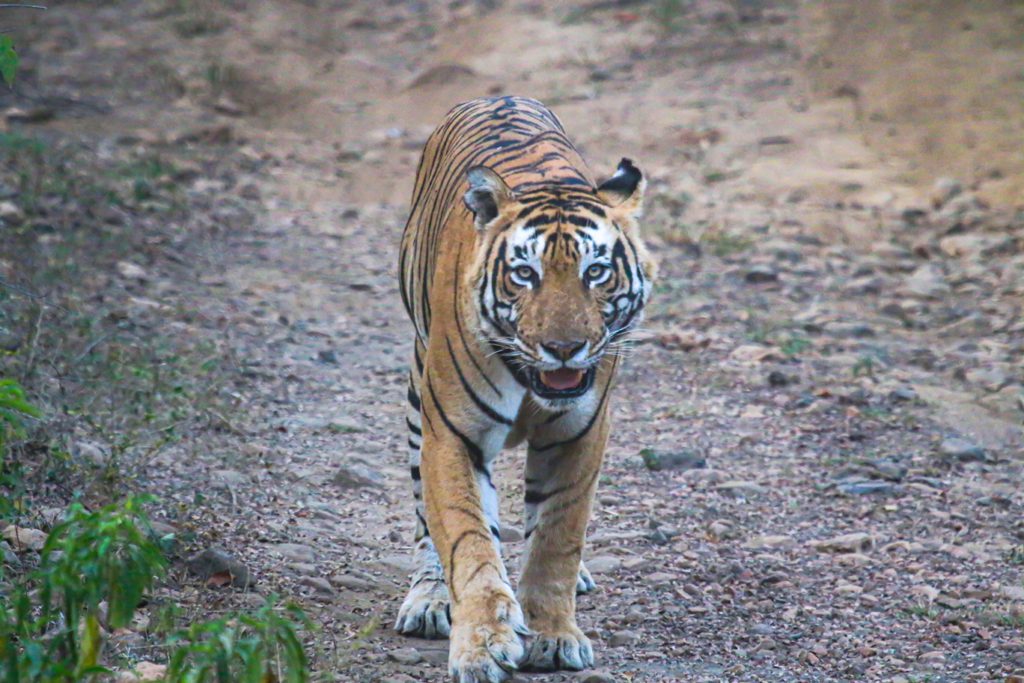
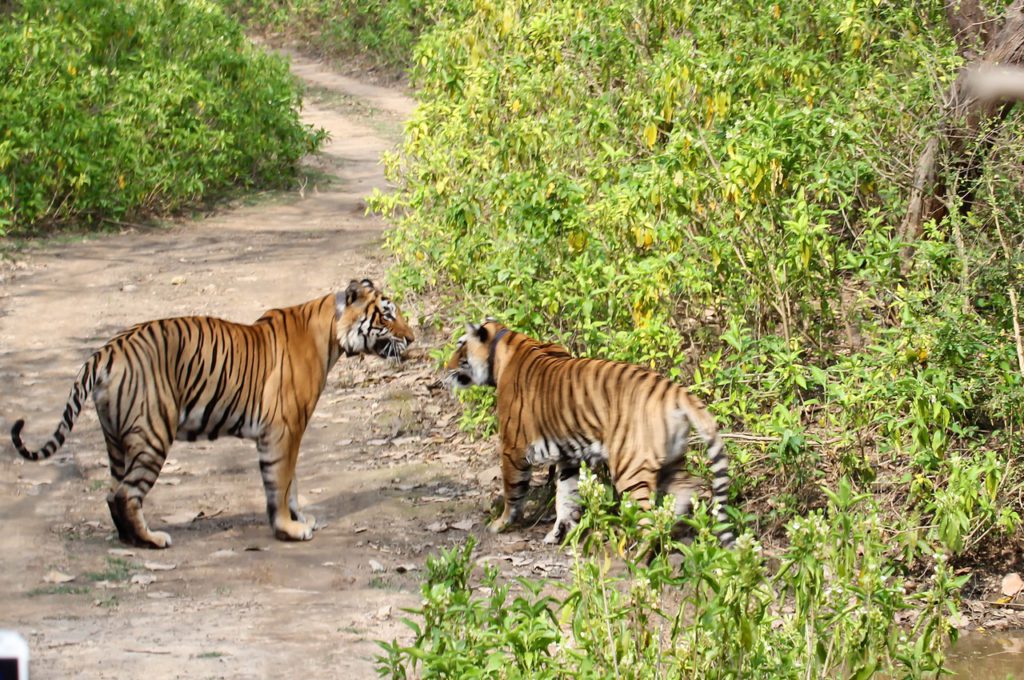
Over the years, photographer and naturalist Devendra Singh has documented the tigers of Sariska National Park. This photo essay chronicles the slow but steady improvement in their population after three individuals were translocated to the Park. The Sariska experience, beautifully captured by his lens, poses lessons for similar exercises in India and across the world.
Located in Alwar District, Rajasthan, Sariska Tiger Reserve used to be the hunting preserve of the Alwar estate. Spread over 880 square kilometres, this has always been an important connector of the Northern India tiger and leopard corridor. The reserve was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1958 and a tiger reserve under the Indian government’s Project Tiger in 1979. Unfortunately, the robust population of around 28 tigers in Sariska was totally wiped out by 2003-04. Most were poached by the infamous Sansar Chand, who probably relied on the support of the local population and the still existing villages within the reserve. Whatever be the case, this unfortunate turn of events led to the vanishing of the apex level predator in the food chain in this area.
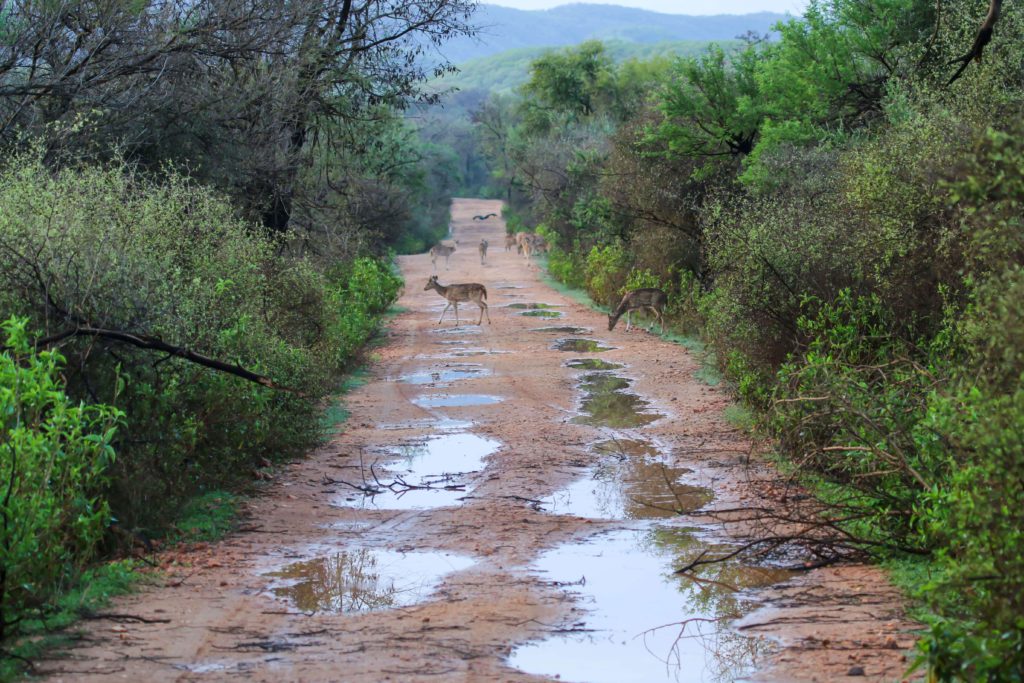
Everything is interrelated in the jungle. The demise of the tiger altered the topography of the park, resulting in a sharp increase in the population of antlers, the erstwhile favorite food of the tiger in the park. This spotted deer that I have photographed looks pretty, batting its ridiculously long lashes, but without the king of the jungle, rising deer populations decimated grasslands and shrubs. The resultant forest degradation made the habitat even more difficult for wildlife to survive and thrive.
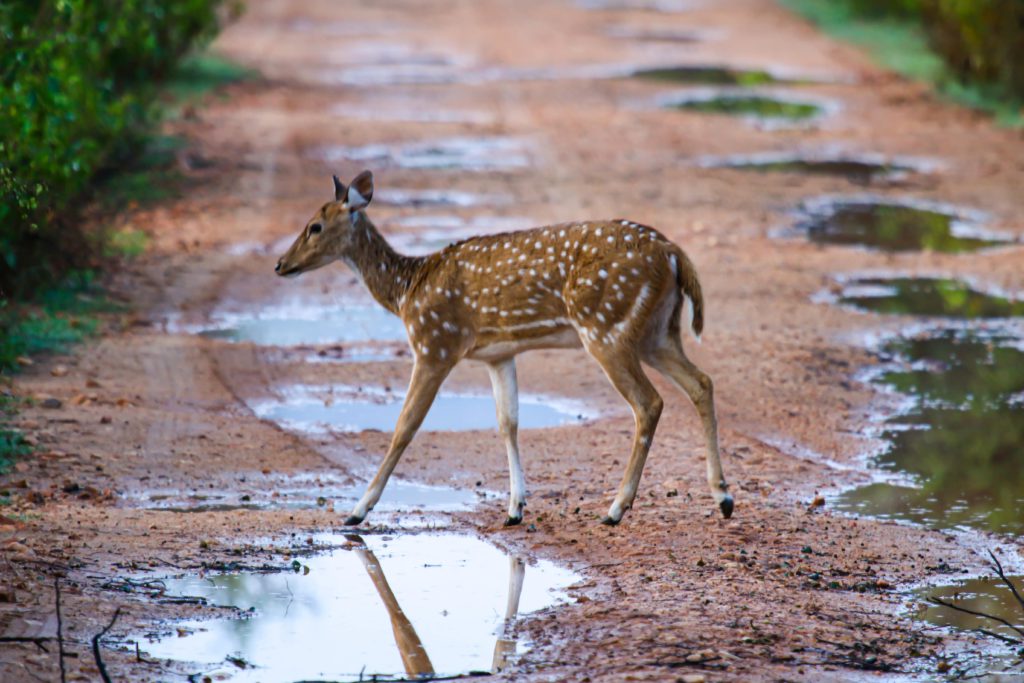

Spotted Deer (Chital)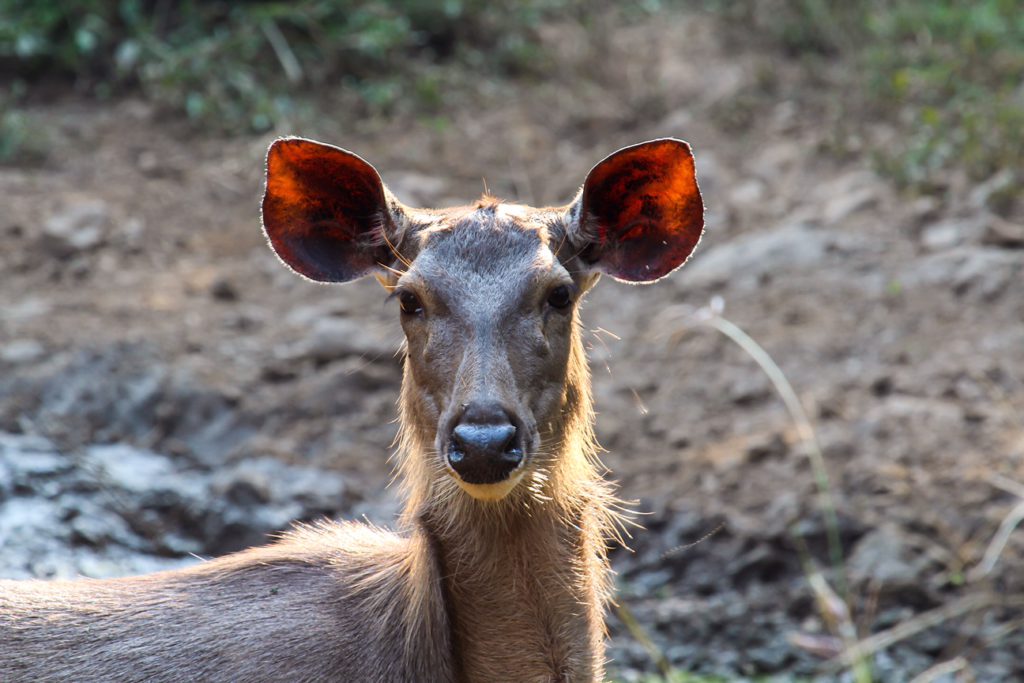 
Female Sambhar Deer
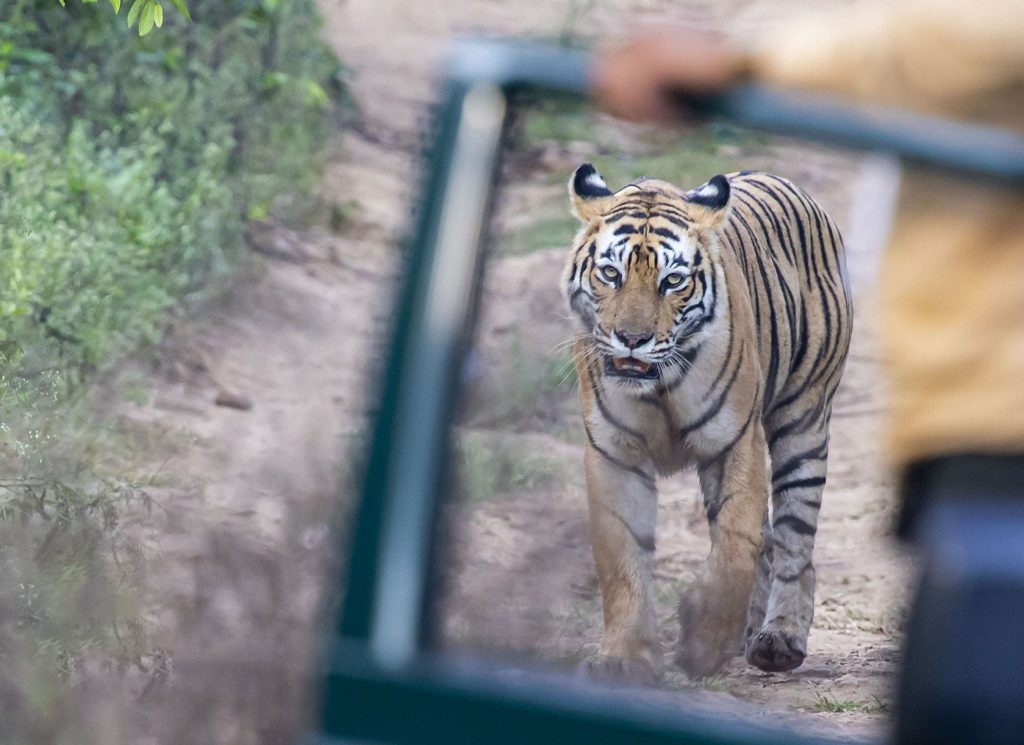
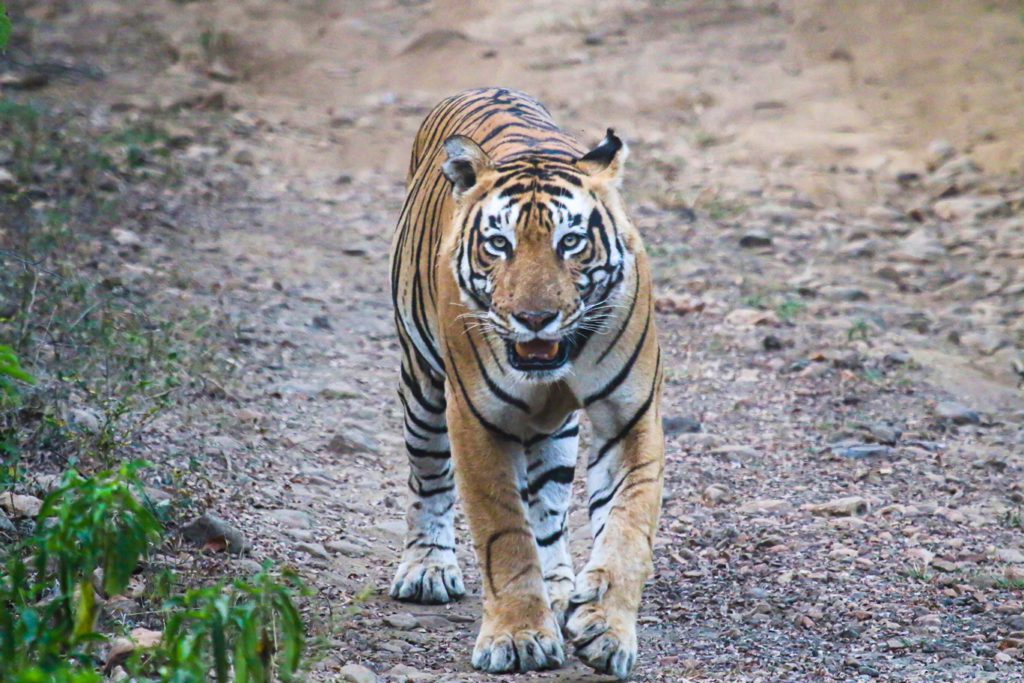
In 2009, Sariska became the first reserve in the world where tigers were successfully relocated. These were the first tigers this thorny, arid scrub forest had seen in years. The joy was, however, short-lived. The first reintroduced male tiger died after feeding on a poisoned cattle carcass and relocated tigresses did not breed as expected. Was the forest too stressed because of human activity for it to regenerate and tigers to flourish once more?
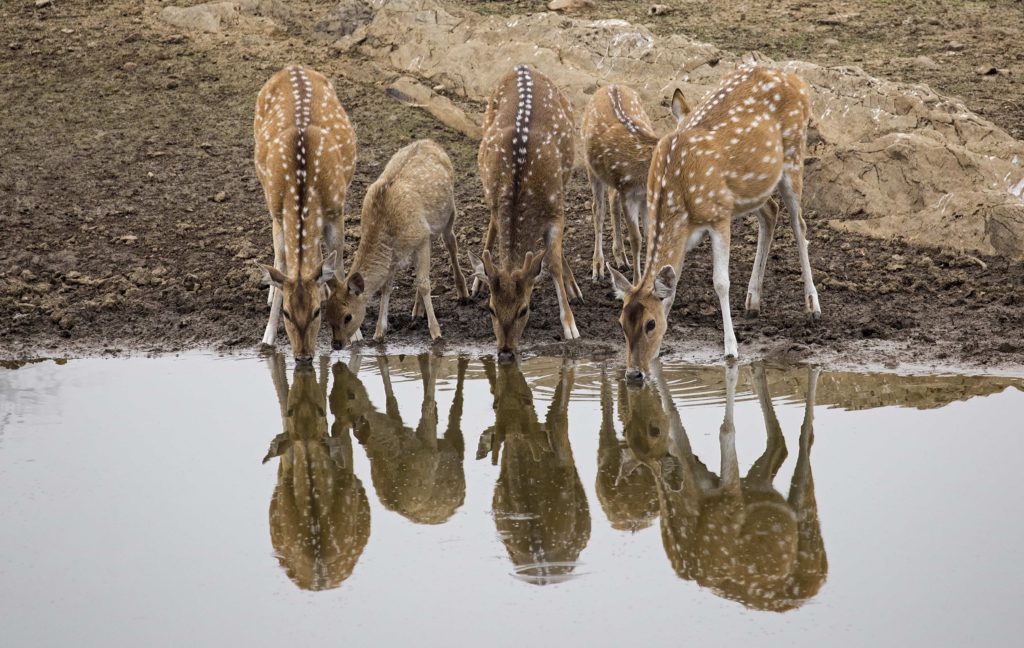

Spotted Deer (chital) at a watering hole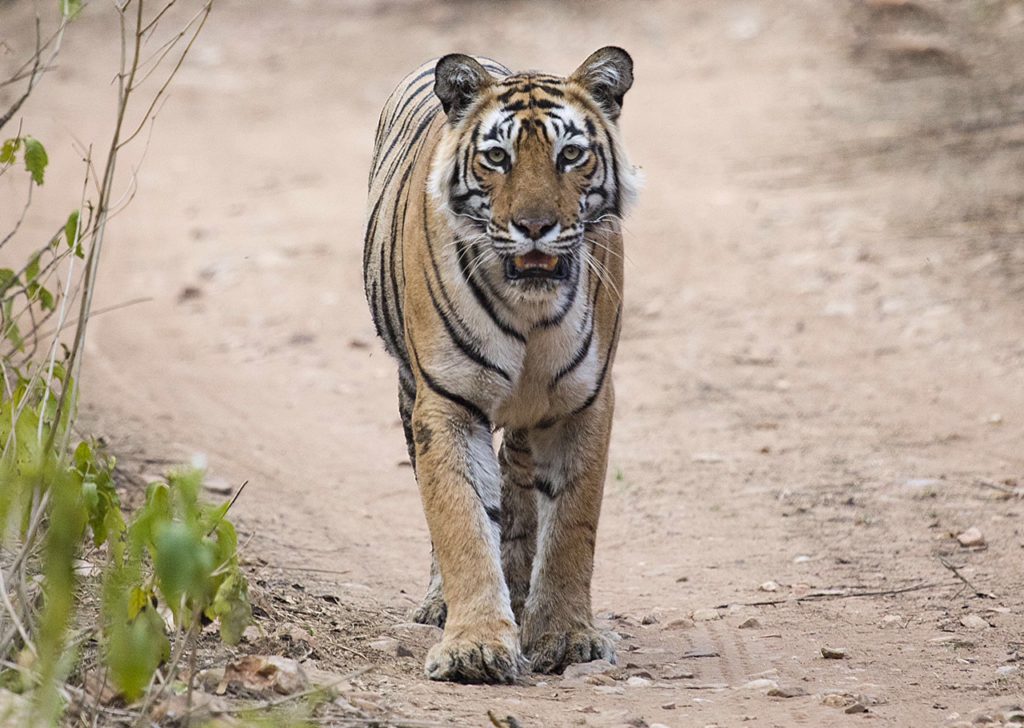 
Things started looking up by 2012, when a female tigress named ST-2 was sighted with cubs. Sansar Chand died in 2014 and poaching activities slowed down. Better forest management techniques were subsequently enforced and big cats started making a slow comeback. Relocation of six villages from the core areas reduced human activity inside the jungle. This improved the habitat and gave tigers much needed space to move about freely.
Sariska has become a success story with the tiger population going up steadily. 23 tigers live here now, including three cubs. The enforced lockdown has given an unexpected and happy boost to the conservation efforts at the Park. This year, I have seen several individuals, including ST9, ST3 and ST6. Since September 2021, ST21 and ST9 have been courting. Hopefully their courtship will herald some good news for conservationists here!

Peacock displaying its feathers 
Peacock
In architecture, the keystone at the top of an arch holds the arch together. Without the keystone, the whole arch and building surrounding collapses! Tigers are regarded as keystone species in their habitat. The return of tigers to Sariska has had an immeasurable impact on its biodiversity and ecological health.
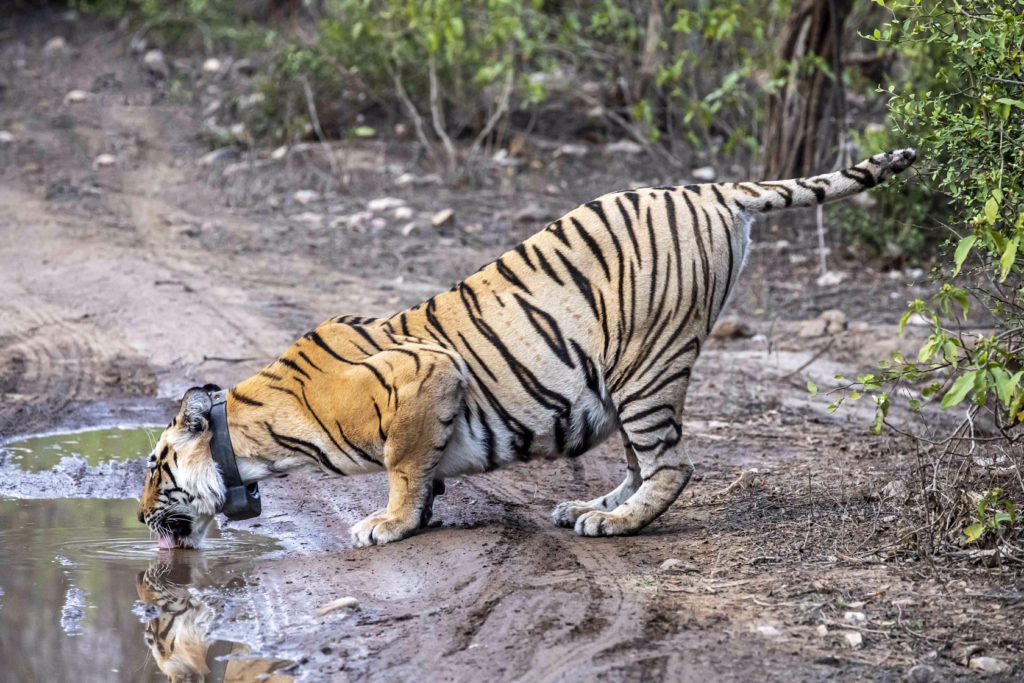
Today, the slow but steady repopulation of tigers in Sariska holds important lessons in the viability of such rewilding programs. Do radio collars around the neck hinder breeding success? Can rewilding be successful in forests with a lot of human activity? Are some tigers more efficient breeders than others? And what can be done to improve the survival rate of tiger cubs? Perhaps the answers to such questions will bring greater focus and success to species reintroduction programs across the world.
In the meantime, Sariska has become my favourite weekend destination from Delhi to get a quick and wholesome experience of these majestic creatures in the wild!
Author: Devendra Singh, The India Story Agency for Sacred Groves
Images Credit: Devendra Singh
Did you enjoy this article?
Share with friends to inspire positive action.