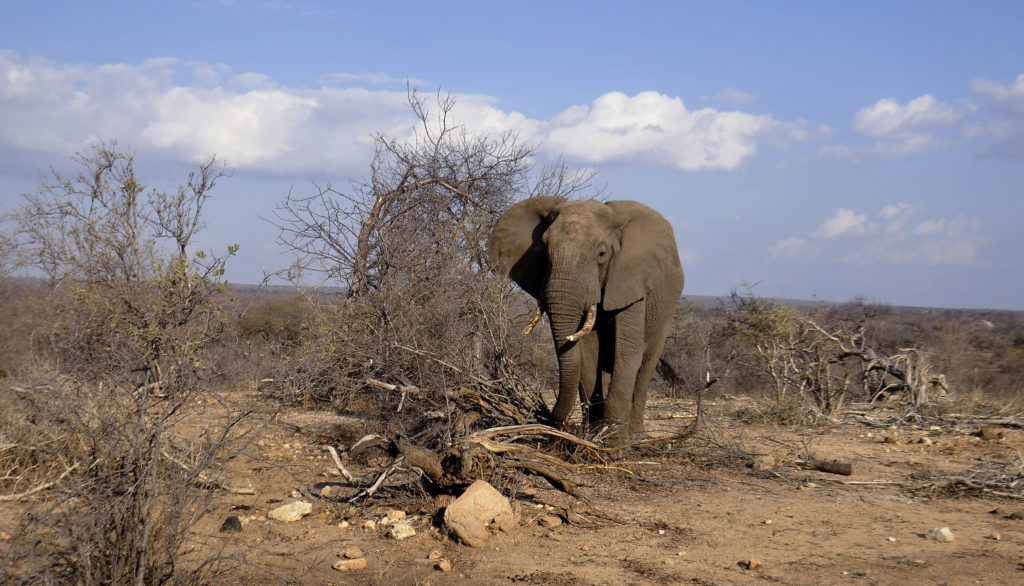
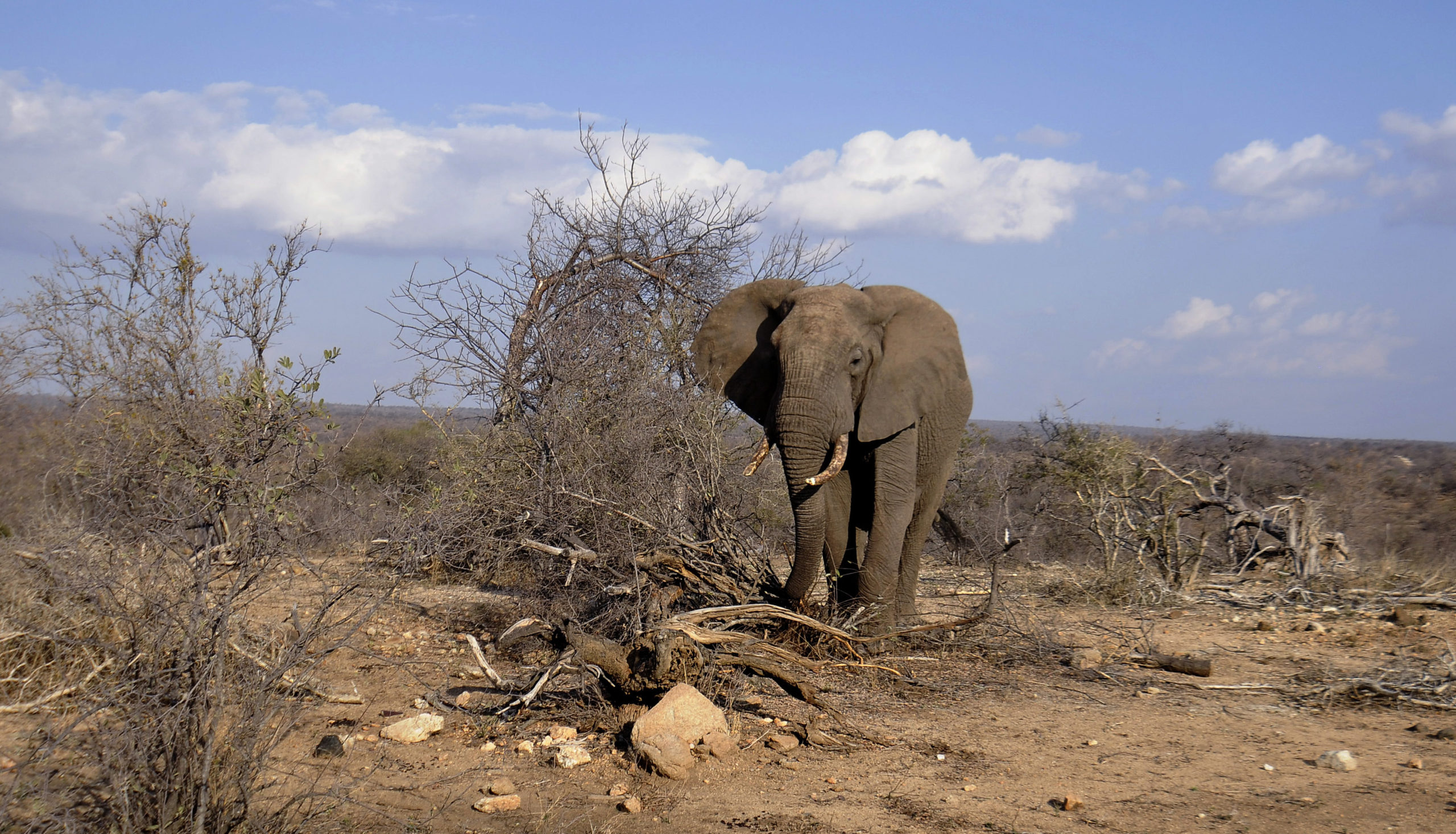
The world’s wildlife rangers lead the fight against wildlife crimes, which include poaching and killing and maiming animals for their tusks and hides. Traditionally male, one all-female unit of rangers are becoming role models in their native South Africa, as they prove women have unique skills to bring to the job.
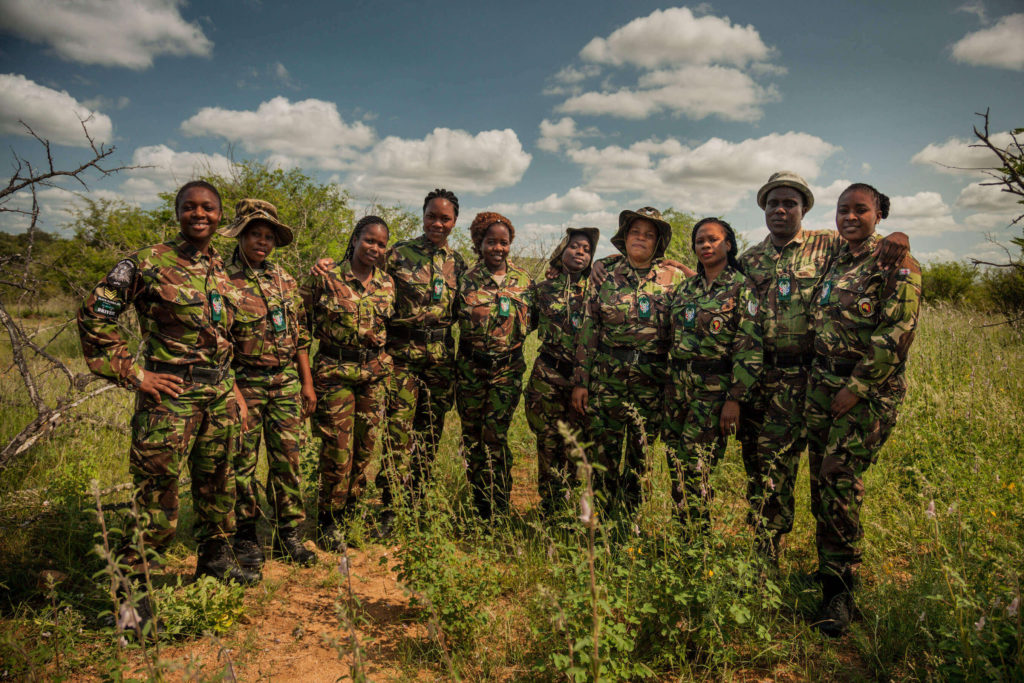

When you find yourself admiring images or footage of rare creatures, do you ever wonder what’s involved in protecting them? Leading the fight against wildlife crime are the world’s wildlife rangers, military-style anti-poaching patrol units for whom conservation is a full-time commitment. In biting cold and searing heat, they cover vast wilderness areas, seizing animal traps and keeping watch for illegal hunting and other suspicious activity. Most of their number – close to 90 per cent – are men. However, as natural communicators and protectors, female rangers tend to punch above their weight.
South Africa’s Black Mambas are a prime example. They’re the not-so-secret weapon of the 62,000-hectare Balule Nature Reserve. As a Big Five reserve situated in an accessible location, Balule has always been vulnerable to poachers. However, the all-woman Black Mambas ranger unit has turned its fortunes around. They patrol the fringes at dawn and dusk, with remarkable success, and run an environmental education programme for local school kids.
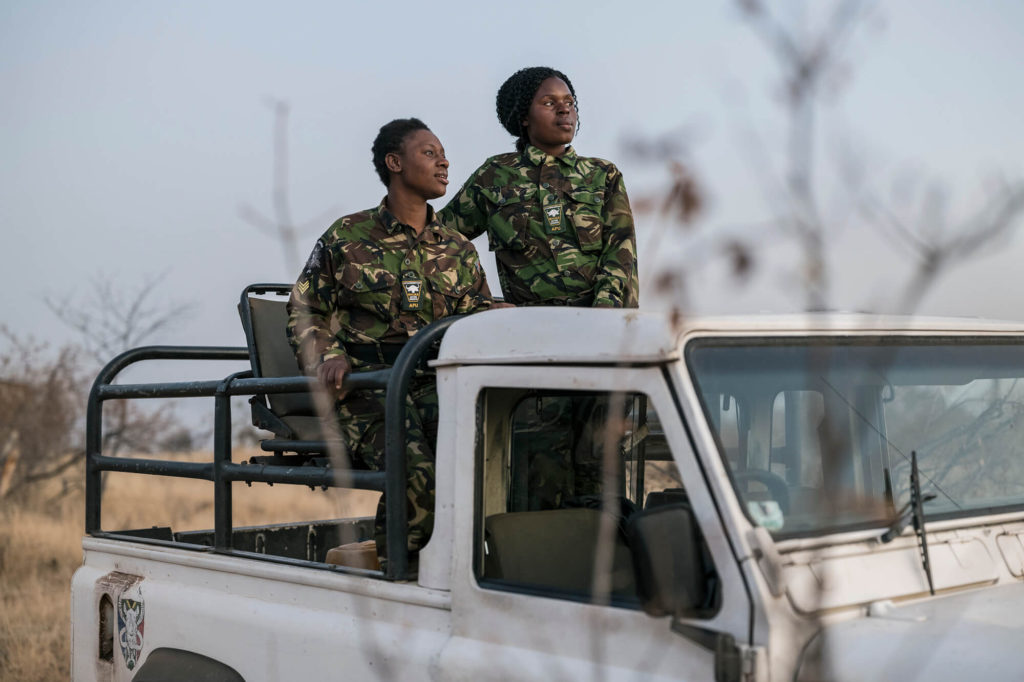

“We are the eyes and ears of the bush,” says unit sergeant Nkateko Mzimba. “We don’t carry guns, just pepper spray, because our job is to gather intelligence and act as a deterrent. This leaves the armed rangers free to concentrate on guarding the animals inside the reserve. If we detect an intruder, we call for back-up.”
Prior to the Black Mambas’ formation in 2013, would-be poachers would enter the reserve every day. “We’ve reduced intrusions by 89 per cent,” says Mzimba. The tough circumstances surrounding Covid-19 haven’t dented their record. To date, the pandemic has claimed relatively few lives in rural Africa, but its indirect effects have been catastrophic. With international travellers largely absent from the safari heartlands, there have been fewer safari vehicles at large and fewer tourist dollars coming in, resulting in an upswing in both opportunistic and organised poaching. But Balule has weathered the storm, thanks in no small part to the Mambas.
Mzimba believes that female rangers bring crucial skills to the job. “Women are better at keeping a secret”, she says. “Gathering intelligence is an important part of our work. When men are off duty, relaxing with their friends, they can be tempted to talk too much and say things they shouldn’t. I think women have more self-control.”
It’s a formula that’s beginning to play out in other parts of Africa. In Zimbabwe, the all-female Akashinga unit patrols elephant poaching hotspot Phundundu, while Kenya’s first women’s unit, Team Lioness, covers Amboseli.
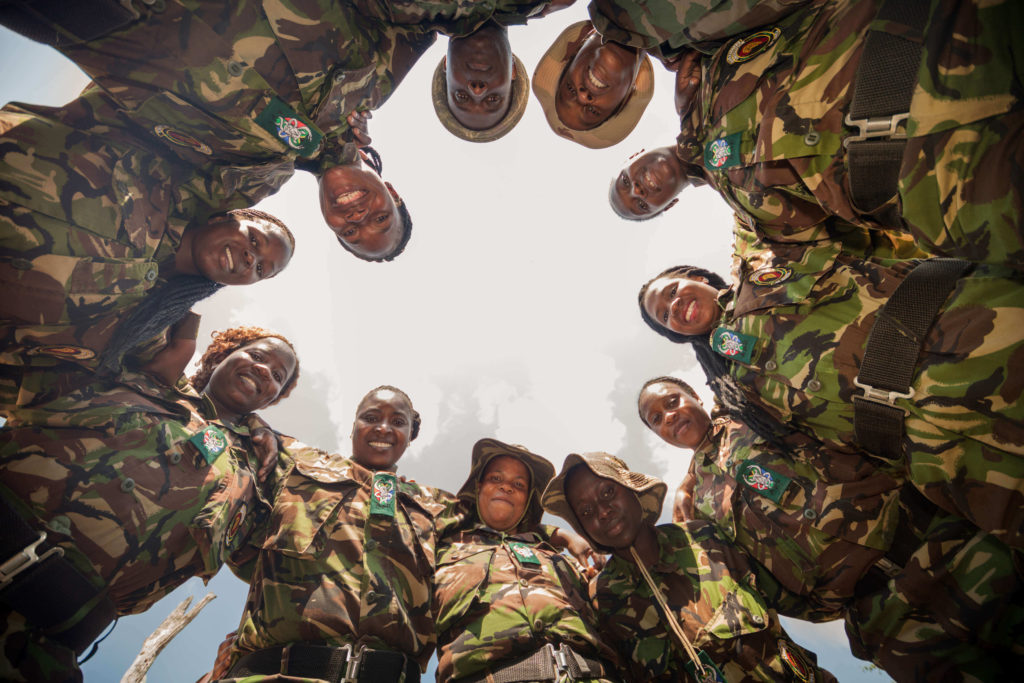

The Black Mambas have become powerful role models within their community and have won awards for their efforts towards the Protection of Wildlife, but British campaigner Holly Budge of conservation initiative How Many Elephants feels units like these deserve far greater international support. To this end, she is launching World Female Ranger Day on 23 June 2021. “This new annual event will celebrate these women, while highlighting the significant gender imbalance in environmental conservation”, says Budge. “We’ll be collating gender-specific data about female rangers, to identify their needs.”
As Black Mamba ranger Leitah Mkhabela puts it, “We cannot do it by ourselves. We need more eyes, more people helping us.”
Author: Emma Gregg, The India Story Agency for Sacred Groves
Images Credit: Bull elephant banner image – Jan Fleischmann/ Wikimedia Commons, other images Ian Godfrey Getty images for Lumix, 3DE Studios
(Wikimedia License – https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode)
Did you enjoy this article?
Share with friends to inspire positive action.